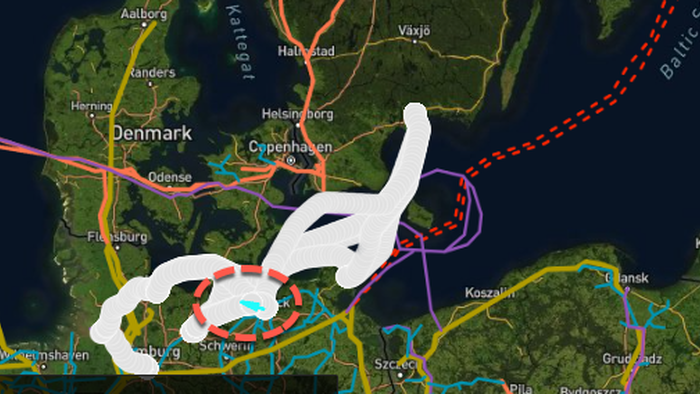
On October 11, 2024, media reports highlighted a major incident involving the German-flagged oil tanker “Annika,” which caught fire off the Baltic Sea coast near Börgerende, northern Germany. The vessel, measuring 73 meters (240 feet) in length, was carrying approximately 640 metric tons of oil when the blaze erupted. Footage shared on social media platform X indicated that flames were initially observed at the stern of the vessel. While reports from AP News and Reuters confirmed that seven crew members were successfully evacuated, the potential causes of the fire remain unverified; officials have yet to disclose whether mechanical failure, human error, or another factor was responsible for the incident.
The response to the fire involved multiple rescue boats and helicopters, as emergency services worked to control the situation on the burning tanker. As news of the fire spread across various social media channels and news outlets, numerous eyewitness accounts described the scene and the efforts of the firefighting teams on-site. It was reported that there have already been several injuries as a result of the fire, although details concerning the extent or nature of these injuries were not immediately clarified by the authorities.
This incident is occurring against the backdrop of heightened geopolitical sensitivities concerning the Baltic Sea region, often referred to as a “NATO lake” due to its strategic importance. The sea is bordered by eight NATO members and features several access points that Russia utilizes. Given these dynamics, the area has become increasingly significant for both military and energy security considerations, especially in a time marked by tensions between NATO countries and Russia. The proximity of critical infrastructure, such as the Nord Stream pipeline, further compounds concerns regarding maritime safety and security in this region.
In light of the ongoing crisis, discussions surrounding maritime safety protocols and emergency response measures are likely to gain prominence. As incidents like the Annika fire unfold, they underscore the need for robust contingency plans in maritime operations, particularly when dealing with hazardous materials like oil. The situation also raises questions about the environmental impact of such accidents, given the large volume of oil on board the tanker. Spill response measures and the potential for ecological damage to the delicate Baltic Sea ecosystem will need to be thoroughly assessed by authorities moving forward.
The incident also highlights the risks inherent in the shipping industry, particularly as global trade continues to expand and ship traffic increases in strategically important waters. With many countries relying heavily on maritime transport for the movement of goods and resources, incidents like the fire on the Annika serve as stark reminders of the vulnerabilities faced by vessels operating under elevated risks. It is likely that the maritime industry will reevaluate approaches to safety and risk management in light of this situation, especially concerning older vessels and those operating under flags of convenience.
As more information is gathered and investigations commence, the focus will remain on the immediate needs for containment, rescue, and support for those affected by the fire. The international shipping community, local governments, and environmental agencies will keep a close watch on the developments following the Annika incident, employing the lessons learned to improve the resilience of maritime operations in the Baltic Sea and beyond. The broader implications of this event on regional safety, security, and environmental protocols could have lasting effects well beyond the immediate crisis at hand.