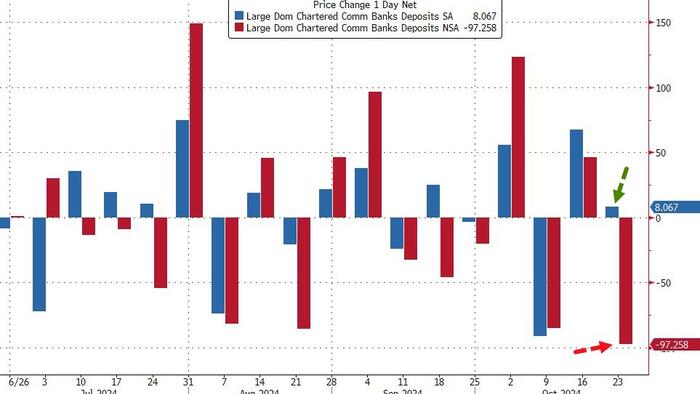
In the latest financial developments, money market funds experienced a significant inflow of $40 billion over the past week, reaching an unprecedented total of $6.508 trillion in assets under management (AUM). This continued inflow reflects a persistent trend towards the safety and liquidity offered by money market funds amidst fluctuating conditions in the banking sector. According to Bloomberg data, the inflows occur simultaneously with a decline in bank deposits, which dropped by a modest $13 billion on a seasonally adjusted basis for the week ending October 23. However, the non-seasonally adjusted figures reveal a drastic and concerning drop of $133 billion, marking the largest weekly decline observed since April.
Delving deeper into the composition of the deposit movements, the situation appears even more critical when factoring out foreign deposits. On a non-seasonally adjusted basis, U.S. deposits fell by $131 billion, another record decline. Breaking this down further, large banks witnessed a reduction of $97 billion in deposits while small banks experienced a decline of $34 billion. Despite this stark reality, the adjustments made by the Federal Reserve indicate a different picture; on a seasonally adjusted basis, domestic deposits only saw a minimal drop of $3 billion, with large banks actually gaining deposits by $8 billion, while small banks lost $11 billion. This manipulation of seasonal data highlights an underlying issue and raises concerns about the actual health of large and small banks.
The substantial decline in bank deposits presents a worrying trend that could trigger liquidity problems within the banking system. Analysts are particularly attentive to this scenario, as a continuous drop in deposits can drastically affect banks’ lending capabilities and overall market stability. The current situation becomes even more complex when considering the broader financial landscape and factors that may exacerbate these liquidity issues. Some financial metrics indicate that credit and liquidity stress are surfacing, as evidenced by the widening spreads in SOFR-Swap rates. Such signals may hint at underlying weaknesses that could lead to potential challenges for banks if the trends continue.
In addition to the worrying deposit figures, another indicator pointing toward liquidity concerns is the drastic reduction in reverse repo usage. Typically a central banking tool to enhance liquidity in the financial system, the recent decline in reverse repurchase agreement activities suggests that market participants may be facing tightening monetary conditions. This shift raises the question of whether these liquidity issues are indicative of broader systemic risks within the banking sector and the economy as a whole. The overall environment, compounded by fluctuating monetary policy and market reactions, demands close scrutiny from analysts and regulators alike.
As the financial landscape evolves, the rising U.S. sovereign risk also draws attention. Increased sovereign risk often indicates market apprehension about the solvency or economic stability of a nation, suggesting that investors may be reassessing their confidence in the U.S. financial system. The interplay between declining bank deposits, rising sovereign risk, and broader market uncertainties can be particularly troubling, creating a challenging backdrop for policymakers who must navigate these turbulent waters without triggering panic among the populace.
Amidst these financial dynamics, speculation arises regarding the implications of these trends in the context of national political narratives. Discussions surrounding the potential for a banking crisis or financial instability become intertwined with conjectures about electoral politics, specifically with regard to Donald Trump’s resurgence in recent public opinion. Some analysts ponder whether the current financial strains, exacerbated by bank deposit declines and sovereign risk evaluations, could be leveraged or manipulated in the political arena. The outcome of these intertwined issues will not only influence economic policymaking but could also have substantial ramifications for the prevailing political landscape as the country approaches pivotal electoral moments.