Google’s Strategic Response to Emerging AI Competitors
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, Google (GOOGL) finds itself at a critical juncture as it navigates the intricate challenges posed by increasingly sophisticated AI models, particularly those developed by competitors like OpenAI and Anthropic. With its commitment to enhancing its AI infrastructure and diversifying its services, Google aims to safeguard its Search revenue, which has already witnessed some disruption. Nevertheless, models like OpenAI’s ChatGPT present significant competition, potentially reshaping Google’s revenue composition over the next decade. Current trends indicate that while Google continues to dominate the global search market with a substantial 90.48% market share, it must take strategic steps to adapt to the challenges of innovative AI solutions that deliver more engaging user experiences.
Despite the formidable rise of AI-driven platforms like ChatGPT, which achieved 100 million users in a mere two months, Google’s Search services remain resilient, generating approximately $49.385 billion in revenue within the third quarter of 2024 alone. This accounts for 55.9% of Google’s total quarterly revenue of $88.3 billion. Yet, with consumers increasingly dipping their toes into AI tools, the potential exists for a shift in user engagement that may lead to a declining share of Search-related revenue over the next five to ten years. As various AI models continue to develop and capture the attention of users for their advanced capabilities—sometimes surpassing Google’s traditional Search functionalities—the urgency for Google to innovate in its service offerings becomes even more pronounced.
The rapid advancements made by AI competitors, such as Anthropic’s Claude and Perplexity AI, further complicate the environment for Google. These firms are building strong partnerships, like Anthropic’s collaboration with Amazon Web Services, to enhance the safety and efficacy of their AI systems. Perplexity AI, on the other hand, is refining academic research tools, delivering more efficient means for users to access information. As casual users experience these AI innovations, it’s conceivable that they may transition from Google Search to more advanced alternatives, potentially undermining Google’s core revenue model. With the global AI market projected to reach approximately $3,680 billion by 2034, Google faces significant long-term risks associated with its traditional operational model.
In response to these emerging threats, Google is strategically investing in its AI capabilities, channeling $13 billion into related infrastructure and platforms as of Q3 2024. This investment is essential for enhancing user experience and ensuring that its services remain competitive. Google’s introduction of AI-powered features, such as AI Overviews and the next-generation Gemini model, emphasizes its commitment to innovation. However, these initiatives must keep pace with rapidly evolving AI capabilities in areas like multimodal interactions and more nuanced query handling to maintain their appeal to users seeking advanced functionalities. While Gemini has showcased some academic advantages over its rivals, practical applications still lag behind what competitors like ChatGPT can offer.
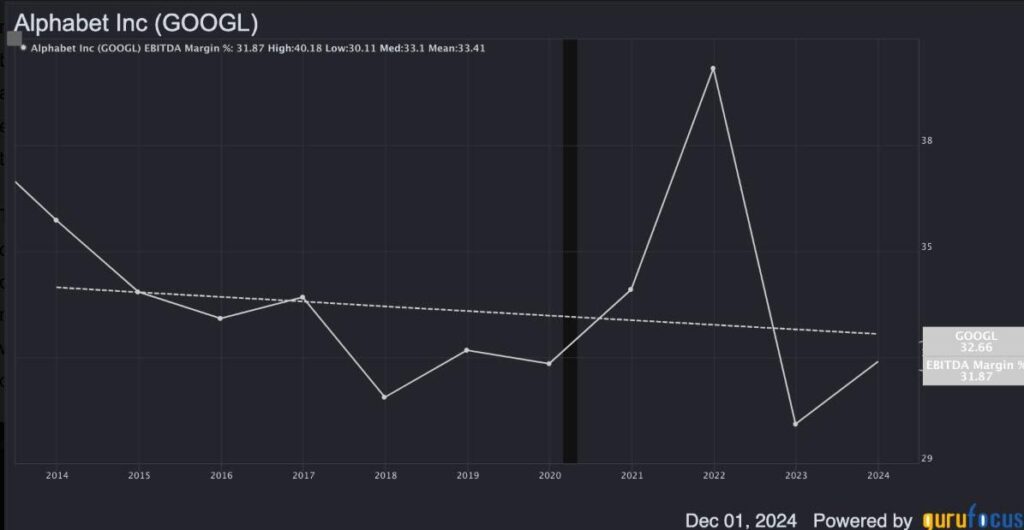
Financially, Google shows a robust outlook despite facing headwinds in its traditional revenue streams. With trailing twelve-month revenues of $339.859 billion, and a five-year historical growth rate of 21.3%, the company is anticipated to achieve a revenue growth rate of 12.5% annually over the next decade. This projection leads to an estimated total revenue of approximately $1.104 trillion by December 2034. Despite a downward trend in its EBITDA margin, potential margin expansions due to AI integration could stabilize earnings, leading to EBITDA projections of $386.271 billion by the same year. When considering an enterprise valuation approach that includes a median EV-to-EBITDA ratio of 15, a significant increase in enterprise value to around $5.794 trillion implies a potential compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.17% over ten years.
In evaluating the overall landscape, one must not overlook Google’s diversified business model, which extends beyond search-focused revenues. The company’s foray into cloud computing, hardware, autonomous vehicles, and health-tech positions it well for long-term sustainability amidst evolving market dynamics. Google Cloud, for instance, has seen impressive year-on-year revenue growth of 35%, a testament to the demand for its AI-related services. While the ascent of AI platforms could challenge traditional revenues, Google’s integral investments and expansion in AI solutions may provide a robust cushion against impending threats to its Search revenue, thus allowing for continued growth in alternate sectors.
In conclusion, Google is currently grappling with transformative challenges posed by AI competitors, particularly in its historical domain of Search. However, with substantial investments in AI innovation and an overarching diversification strategy, Google is poised to adapt to shifting consumer preferences. Although the threat remains significant, the calculated strategic maneuvers employed by Google can facilitate a transitional evolution of its revenue streams over time. My conservative valuation model indicates an 11% margin of safety, supporting a Buy rating for Google shares. As the company navigates the carefully balanced demands of maintaining its Search leadership while expanding into broader AI applications, it is likely to emerge resilient in a future replete with opportunities in AI-driven solutions.