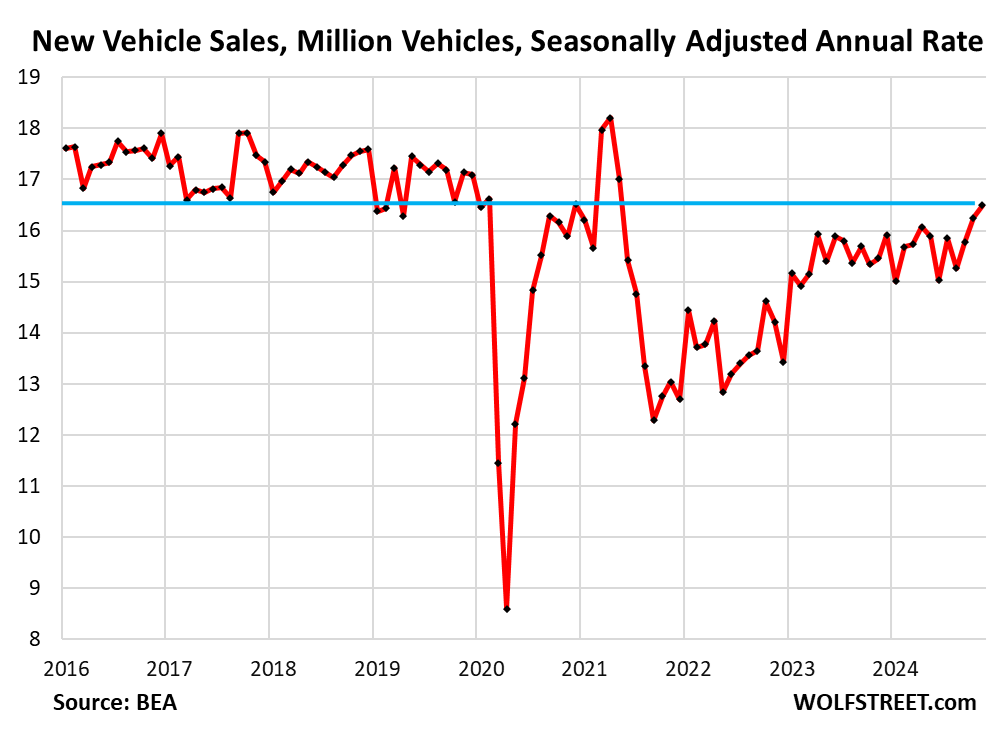
In November 2023, the automotive market demonstrated a resurgence, witnessing a significant increase in total new-vehicle sales, which rose by 10% year-over-year to 1.40 million units. This increase can largely be attributed to an additional selling day compared to the previous year, as reported by the Bureau of Economic Analysis. When isolating retail sales—excluding fleet deliveries—the data from J.D. Power indicates a similar growth pattern, with retail sales also experiencing a 10% year-over-year increase to 1.15 million units. Notably, the seasonally adjusted annual rate of sales has reached 16.5 million vehicles, a level not seen since May 2021 when semiconductor shortages severely impacted availability. With inventory levels more than doubling since then, a price-cutting phase is considered inevitable as automakers work to attract consumers amid ongoing economic fluctuations.
The sales boost is partly fueled by aggressive incentives and discounts from automakers aiming to motivate purchase decisions due to the excess inventory accumulated over the past year. Despite some models still being in limited supply, the overwhelming trend is clear: high vehicle prices, exacerbated by pandemic-related price hikes, are beginning to soften. The projection for total vehicle sales in 2024 has been raised to 15.93 million vehicles, rebounding to levels not seen since 2019. However, it is important to acknowledge the auto industry’s long history of stagnation in unit sales, which have remained flat for over 25 years, punctuated by occasional downturns. Meanwhile, certain brands like Tesla and Hyundai-Kia have seen substantial sales growth, capturing significant market share from traditional manufacturers whose sales have dwindled.
The state of new-vehicle inventories has also shifted dramatically, surging to 3.04 million vehicles in early November, marking the highest levels since May 2020, according to Cox Automotive. This oversupply has effectively driven the average incentive spending by automakers up by 43% year-over-year to $3,291 per vehicle, accounting for 6.5% of the manufacturer’s suggested retail price (MSRP). Notably, leasing has contributed to this increased incentive spending, comprising 23% of retail sales in November. While current incentives serve to temporarily stimulate the market, there is still potential for further increases. For instance, in 2019, incentives peaked at 10% of MSRP, indicating room for more aggressive discounting in response to the current stock levels.
Ford Motor Company exemplifies the industry trend by reporting a 14% increase in sales for November. Their battery electric vehicle sales surged by 20%, alongside a variety of promotional offers such as zero-percent financing and cash rebates. Ford has also made significant adjustments to pricing, notably reducing the MSRP for the 2025 F-series models upon their debut, representing the first such price cut in decades. Meanwhile, Stellantis faced challenges relating to their pricing strategies, leading to a dealer outcry and subsequent adjustments for overstocked vehicles, prompting the launch of larger incentives and discounts. This shift underscores the broader acknowledgement within the industry of the need to recalibrate pricing strategies in response to market demand.
As the downward pressure on prices and increasing affordability of vehicles take shape, experts predict that these trends may promote sustained momentum in new vehicle sales. J.D. Power notes the potential for improvements in vehicle availability while transaction prices and overall profitability are anticipated to shift slightly lower. Additionally, the Consumer Price Index (CPI) for new vehicles has shown a slow but steady decline over the last two years, following a significant spike during the pandemic, although much more gradual than the rapid fall observed in used vehicle prices. This persistence in new vehicle prices contributes to the broader discussion surrounding affordability in the current economic landscape.
In summary, the automotive market appears to be at a critical juncture, where a build-up of vehicle inventories, rising incentives, and evolving sales strategies signal a shift from inflated prices to a more competitive pricing environment. Brands are increasingly recognizing the necessity to adapt to changing consumer sentiment and market dynamics, aiming to capture sales momentum while addressing the long-term structural challenges that have plagued the industry. The convergence of these factors will likely define the landscape of the automotive market in the near term, shaping consumer experiences and the financial viability of manufacturers as they navigate this complex terrain.