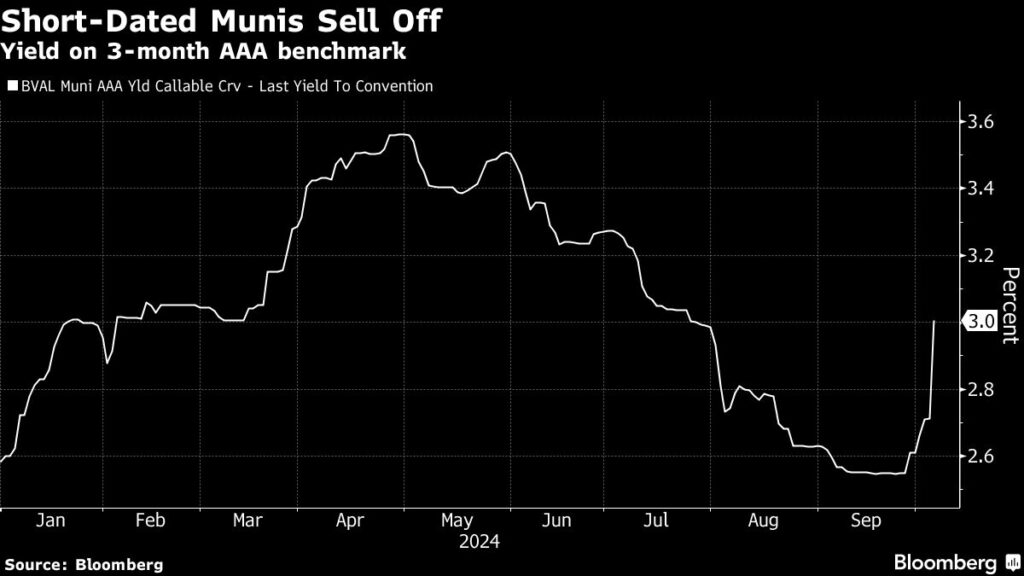
The recent sell-off in the shortest-dated municipal bonds is primarily attributed to a robust employment report that has prompted investors to reassess the likelihood of significant interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve. Yields on three-month AAA municipal bonds surged by 29 basis points in a single day—the most substantial increase since 2022—reflecting the influence of resilient labor market data indicating the continuing strength of the US economy. This shift has resulted in shorter-term municipal yields surpassing those of AAA-rated bonds maturing in 16 years, reinforcing a notable inversion in the municipal yield curve. This inversion has persisted for over two years since the Federal Reserve initiated its rate hike cycle in 2022, and while there were indications of a potential normalization, the latest employment data has disrupted traders’ expectations regarding the Federal Reserve’s future easing policies.
The sell-off in municipal bonds extended into the following Monday, with the 10-year AAA benchmark yield climbing by three basis points. This indicates a broader response in the municipal market to changes in investor sentiment guided by economic indicators. Mikhail Foux, who leads municipal research and strategy at Barclays Plc, noted the correlation between the municipal market’s performance and the movements in the U.S. Treasury market. He emphasized that the reactions in the municipal sector tend to be derivative of the Treasury market, suggesting that any shifts in expectations about Federal Reserve rate cuts will have a consequential impact on the front end of the municipal yield curve.
Chad Farrington from DWS Group echoed Foux’s sentiments, emphasizing that the short end of the municipal curve, particularly bonds maturing in under five years, would closely follow the Federal Reserve’s policy direction. This indicates that market perceptions of the Fed’s future actions are significantly influencing short-term bond prices. Interestingly, while longer-dated municipals have shown better performance relative to Treasuries, this trend may result from the inherent lag in municipal debt reacting to shifts in Treasury yields.
Analysts from JPMorgan Chase & Co. predict that municipal bonds are likely to align with the broader upward trend in Treasury yields, especially given the anticipated surge in supply stemming from upcoming presidential elections in November. The expectation is that tax-exempt rates will adjust higher alongside the U.S. Treasury market, driven by this increased supply and investor sentiment surrounding the economic landscape. The combination of heightened supply and evolving investor expectations regarding Federal Reserve policies could exert downward pressure on municipal bond prices as the election approaches.
The current dynamics within the municipal bond market encapsulate a complex interplay between economic indicators, investor sentiment, and Federal Reserve policies. As the market grapples with the implications of a stronger labor market and the potential for continued interest rate adjustments, traders are closely monitoring these developments to gauge the trajectory of bond yields. The recent sell-off, primarily impacting shorter-duration bonds, further illustrates the sensitivity of the municipal market to macroeconomic trends and central bank actions, highlighting the challenges faced by investors in navigating this evolving landscape.
In summary, the municipal bond market is currently experiencing a notable sell-off, primarily driven by robust employment figures that have shifted investor expectations regarding Federal Reserve interest rate cuts. The inversion of the municipal yield curve reflects a complex interaction of short and long-term yields, influenced heavily by the moves in the Treasury market. With analysts predicting alignment with Treasury trends and anticipating a surge in bond supply ahead of the presidential election, the outlook for municipal bonds remains uncertain as investors recalibrate their strategies in response to the evolving economic landscape.