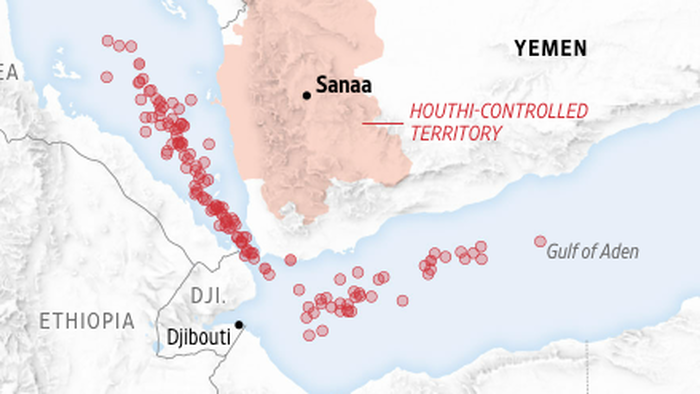
In recent developments in the Middle East, allegations have surfaced that Russian intelligence officials are collaborating with Iranian-backed Houthi rebels by providing them with geospatial intelligence (GEOINT) data. This information is reportedly being utilized for strategic planning and operational decision-making concerning attacks on Western vessels in the southern Red Sea, a vital maritime route. The Wall Street Journal highlights that the Houthis began ramping up their attacks late last year in response to the Gaza conflict and have increasingly incorporated Russian satellite data into their operations. This GEOINT support appears to flow through the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), which has embedded personnel with the Houthis in Yemen. However, specifics about the nature of the GEOINT data provided by Russia remain unclear, particularly whether it includes satellite imagery or real-time data from unmanned aerial vehicles for tracking commercial ships or guiding missiles.
The introduction of Russian support may illuminate why the Houthis have fortified their capabilities in launching missile and drone attacks across the southern Red Sea and Gulf of Aden. Notably, since November 2023, the rebels have reportedly targeted over 100 vessels in the region, with incidents leading to two ships sinking and another being hijacked. This escalation points to a significant expansion of the Houthis’ operational reach, potentially enabled by the sophisticated surveillance and targeting capabilities that GEOINT provides. The implications of this collaboration are profound, not only for regional security but also for international maritime operations, as the growing threat from the Houthis complicates freedom of navigation in one of the world’s most crucial maritime chokepoints.
The evolving dynamics of Russian involvement in Middle Eastern geopolitics signify a critical shift in strategy for Moscow. Traditionally, Russia maintained a complex relationship with Israel; however, under President Vladimir Putin, there appears to be a pivot toward strengthening alliances with Iran. This strategic realignment is observed as Russia enhances its support for Iran’s proxies in the region, positioning itself as a primary ally of the Houthis amidst the ongoing conflict in Yemen and broader tensions involving Israel. The realignment not only affects Israel’s security calculations but also alters the broader balance of power in the Middle East, further complicating the geopolitical landscape.
The situation has been amplified by criticisms directed at the Biden-Harris administration’s foreign policy approach, which many argue has been insufficiently robust to handle the escalating threats from the Houthis and other regional actors. Detractors assert that this perceived weakness has contributed to a broader deterioration of security in the Middle East, which is now marked by persistent unrest and conflicts. The failure to respond decisively to Houthi aggression has led to severe repercussions for global shipping, as rising tensions forced shipping companies to reroute vessels around the Cape of Good Hope, significantly impacting supply chains and escalating costs. Critics highlight that the current administration’s stance reflects a departure from the decisive action that is deemed necessary to maintain stability in the region.
The geopolitical instability in the Middle East is echoed by concurrent tensions in Eastern Europe, particularly regarding the conflict in Ukraine. Observers point out that as international crises multiply, including the precarious situation with China potentially exerting its influence over Taiwan, the world seems closer to a larger military confrontation than in prior years. This interconnectedness of global conflicts raises concerns among security analysts, as they warn that weak leadership on the part of the United States may inadvertently embolden hostile regimes and non-state actors alike. The call for a stronger American response reflects a broader yearning for decisive diplomatic and military actions that prioritize peace and stability in an increasingly volatile global context.
In conclusion, the alleged Russian support to the Houthis marks a significant turning point in the regional power dynamics and underscores the complexity of contemporary geopolitics. As various nations vie for influence in the Middle East, the response from the U.S. and its allies will be crucial in determining the trajectory of future conflicts and ensuring the protection of vital maritime routes. The transitioning relationships between major powers, along with ongoing and overlapping crises, call for a reevaluation of foreign policy strategies that not only seek to promote national interests but also work toward achieving a sustainable and secure international order. Without a coherent and assertive response, the potential for wider conflict looms large, raising questions about the future of global security in an era of heightened rivalries.