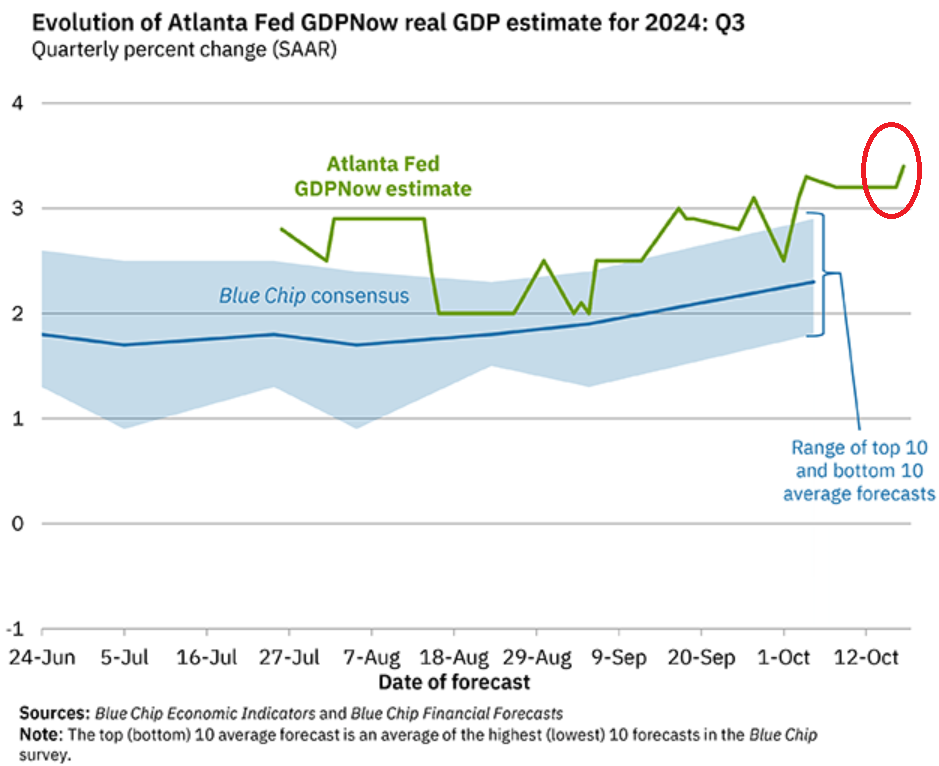
In recent months, the United States has seen an unexpected surge in demand growth, contributing to inflationary pressures. This growth has been fueled, in part, by significant immigration waves between 2022 and 2024, leading to a rise in consumer spending. The release of the retail sales data has prompted the Atlanta Fed’s GDPNow to adjust its estimate for inflation-adjusted GDP growth in the third quarter (Q3) to an impressive 3.4%. The uptick in consumer spending is a strong driver of this growth, with retail sales increasing by 0.4% in September compared to August, along with upward revisions for July and August retail figures. The three-month average retail sales growth now stands at 0.6%, suggesting an annualized growth rate of approximately 7%, adjusted for inflation.
Notably, inflation-adjusted retail sales growth appears even more robust due to declining prices in various retail goods, particularly gasoline and durable goods such as vehicles and electronics. While food prices remain an exception, many other categories have experienced deflation since mid-2022, which positively impacts inflation-adjusted consumer spending. The analysis notes that the ten-year average inflation-adjusted annual GDP growth in the U.S. stands at around 2%, and if Q3 growth aligns with the Atlanta Fed’s estimate, it would mark a quarter of significantly elevated growth. The previous four quarters of real GDP growth also exceeded normal levels, demonstrating a trend of upward revisions in consumer income, spending, and savings.
A contributing factor to this heightened economic activity is the influx of immigrants, which has added approximately 6 million people to the U.S. population recently. According to the Congressional Budget Office, this trend continued into 2024. These new residents engage in the labor market, contributing to retail sales even if their spending habits tend to be more modest. Their frugality, however, still impacts certain categories, including food and beverage outlets, as well as general merchandise stores like Walmart. The three-month sales averages for September have shown a consistent upward trajectory across various retail sectors, highlighting a recovery in consumer behavior after a prior slowdown in spending.
The retail landscape reveals diverse performances across categories. For instance, sales at new and used vehicle dealers, which account for almost 19% of total retail, reached $134 billion, reflecting a monthly increase of 1.3% and a slight 0.7% rise year-over-year. In contrast, the e-commerce sector, representing 17% of retail, saw sales of $124 billion, growing by 0.6% month-over-month and 7.0% year-over-year. The food services sector has regained momentum after experiencing a decline earlier this year, with September sales climbing to $96 billion, a 0.7% rise from August and a 3.7% increase from the previous year.
Additionally, food and beverage stores reported $84 billion in sales, showing a modest monthly increase of 0.5% and a year-over-year rise of 2.3%. General merchandise stores, excluding department stores, achieved sales of $65 billion, reflecting a month-over-month growth of 0.4% and a pre-existing annual increase of 3.1%. Conversely, gas stations have been adversely impacted by fluctuating gasoline prices, resulting in September sales of $52 billion—a 0.8% decrease from August and a 5.6% drop year-over-year. This trend underscores the relationship between dollar-sales at gas stations and the cost of gasoline, further contributing to the observed inflationary dynamics.
Other retail categories also displayed varied trends, as building materials and garden supply stores recorded $41 billion in sales, marking a month-over-month increase of 0.4% and a year-over-year increase of 0.2%. Similarly, clothing and accessory stores generated sales of $26 billion, reflecting a 0.3% rise from the prior month and a yearly growth of 2.3%. Meanwhile, miscellaneous retailers, including specialty stores like cannabis shops, reported a robust increase of 7.1% year-over-year, boosted by recent price hikes after earlier declines. This diverse performance across retail segments illustrates the complexity of the current economic landscape, shaped by factors such as consumer sentiment, inflation, and the evolving demographic profile of the United States.
Overall, the combination of strong retail sales, positive revisions in GDP estimates, and the significant role of immigration in shaping consumer behavior suggests an economy operating at a higher speed and altitude than the historical norm. However, with this growth, concerns surrounding inflation persist. The data signals a potentially dynamic economic environment in which traditional paradigms of growth and inflation could be redefined in light of current consumer behaviors and immigration patterns. As this situation evolves, it raises important questions about the long-term sustainability of these growth rates and the potential implications for monetary policy and inflation management going forward.