Intel’s stock has experienced a significant decline, dropping over 50% year-to-date, primarily due to disappointing earnings reports in Q2 that fell short of revenue projections. This negative sentiment has been exacerbated by Intel’s inability to surpass key competitor Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) in manufacturing capabilities. Despite these challenges, analysts believe that 2025 could serve as a turnaround year for Intel as the company has made substantial investments in expanding its manufacturing capacity. If management can effectively ramp up its advanced 18A semiconductor technology and capitalize on its manufacturing position, the company’s market capitalization could see an increase of approximately 50% within the next year.
Over the past few years, Intel has faced mounting challenges, underscored by management’s announcement of a $10 billion cost-reduction strategy, which includes workforce cuts and dividend suspensions. This operational restructuring is anticipated to set the groundwork for recovery in 2025. While Intel has struggled against competitors such as AMD and NVIDIA in the chip market, the company continues to receive interest from investors, as evidenced by Apollo Global Management’s proposal for a $5 billion investment. The initiation of the 18A manufacturing node and the company’s IDM 2.0 initiative aims to strengthen its foundry services and overall production capabilities, supporting a potential recovery in market sentiment.
However, it is important to recognize that TSMC maintains a formidable lead in the semiconductor foundry space, holding over 60% of the market share—vastly outpacing Intel and its competitors. Although the upcoming launches of products leveraging the 18A technology may generate growth in the short term, analysts caution against expecting consistent, high growth rates in the future due to intense competition. For instance, while a potential year-over-year earnings growth of over 300% is forecasted for 2025, the semiconductor industry’s cyclicality suggests that such growth may not be sustainable in the long run.
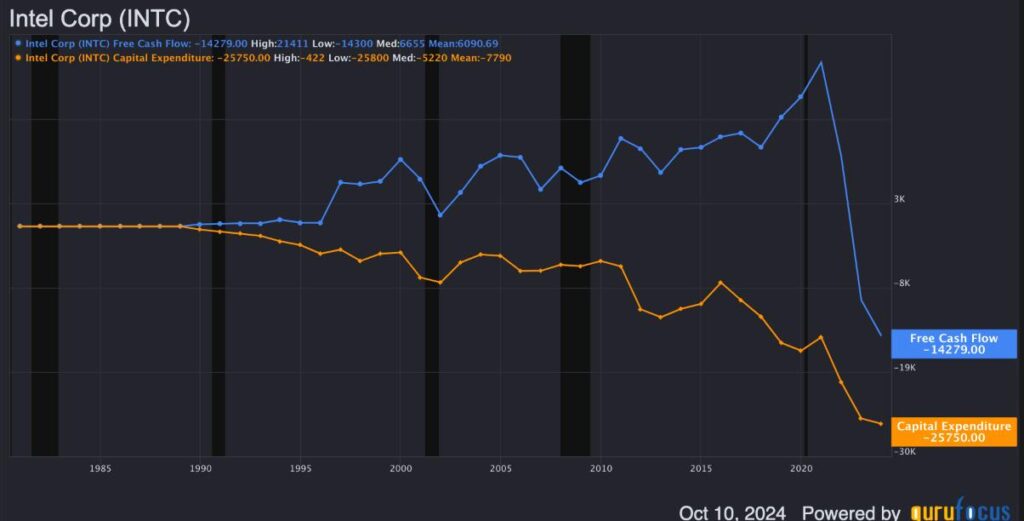
From a financial perspective, Intel’s valuation appears attractive in light of its current stock price, which reflects the vulnerabilities surrounding profitability and market share. Nevertheless, there is optimism about the company’s potential for revenue growth in FY25. Despite challenges in generating stable profits—with net margins having plummeted from over 25% in 2021 to merely 1.8% recently—Intel’s new foundry model is expected to result in significant cost reductions by 2025. While short-term valuation could reflect an appealing opportunity, investors should remain cautious regarding Intel’s long-term prospects due to its operational challenges and competitive landscape.
Intel’s recent setbacks also present execution risks that could hinder the validity of growth forecasts. Delays in constructing major chip-making factories and a significant reduction in workforce create uncertainties surrounding the company’s ability to capitalize on projected market opportunities. Given the rapid advancements in semiconductor technologies led by TSMC and other competitors, Intel’s operational inefficiencies could risk relegating it to a value trap rather than a growth-oriented investment. The company’s strategic initiatives and management execution are crucial for improving performance and overall investor sentiment.
In summary, while there is a strong value opportunity for Intel, particularly with an optimistic outlook for FY25, long-term investment remains precarious due to ongoing competition and operational risks. The potential for a market cap increase of around 50% in the near term remains encouraging, but investors need to stay alert to the competitive pressures and challenges posed by dominant industry players like TSMC, AMD, and NVIDIA that could undermine Intel’s recovery and growth strategies over the next five to ten years.