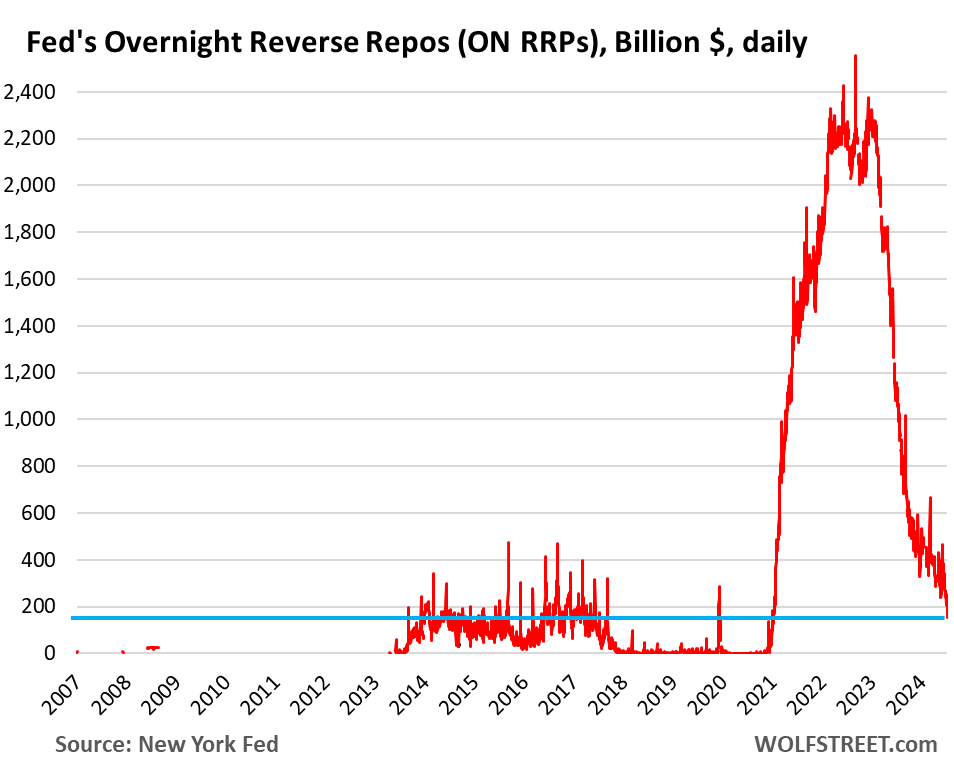
In recent trends observed in the financial markets, Overnight Reverse Repurchase Agreements (ON RRPs) have significantly decreased to $155 billion, marking the lowest level since April 2021. This figure represents a notable drop from the $2.3-trillion range that persisted from May 2022 until June 2023. Additionally, this decline continues a downward trajectory that began after reaching a peak of $2.4 trillion at the end of December 2022. The ON RRP balances reflect cash deposits predominantly from money market funds seeking to earn interest from the Federal Reserve (Fed). These deposits are part of the Fed’s broader monetary policy framework, which recently saw interest rates set at 4.8% following a cut implemented on September 18, 2023. The reduction in ON RRP balances demonstrates the Fed’s continued efforts to drain excess liquidity in the financial system, which had been created during its quantitative easing (QE) phase.
The spikes in ON RRP balances tend to occur at quarter and year-end, primarily driven by window-dressing activities. With approximately $6.5 trillion now in money market funds, and only $155 billion deposited at the Fed, these funds actively scan for better returns. As such, they explore alternate options such as Treasury bills and entering the repo market for lending opportunities. This shift signifies that money market funds prioritize maximizing earnings while adhering to liquidity standards and regulations. ON RRPs serve as a significant tool for these funds as they assess where their cash can generate optimal returns while meeting regulatory compliance.
The primary goal of the Fed’s Quantitative Tightening (QT) initiative is to reduce the overall liquidity in the financial system by pushing ON RRP balances down to negligible levels and moderating reserve balances from their current “abundant” state to a more “ample” condition. While ON RRP balances have witnessed a decline, reserve balances have remained stable at approximately $3.24 trillion since mid-2022, reflecting the slow pace of QT. Before the beginning of QT, reserve balances diminished as funds transitioned from banks to money market funds. Thus, a significant drop in reserve balances has yet to materialize, indicating that QT has considerable ground yet to cover in its efforts to recalibrate liquidity in the financial system.
Dallas Fed President Lorie Logan recently emphasized the relevance of temporary rate pressures in redistributing liquidity within markets. In her comments, she noted that such pressures serve as essential price signals that help allocate resources effectively to areas in need. Logan’s insights draw attention to the function of temporary rate fluctuations in the overnight borrowing markets, suggesting that financial markets are beginning to respond positively to changing liquidity conditions. As rates fluctuate, they reflect evolving dynamics in the market, indicating diminished excess liquidity while prompting physical liquidity reallocation to appropriate niches within the system.
Moreover, trends in the overnight funding markets indicate that rate shifts, predominantly during month-end and quarter-end periods, have started gaining traction. The New York Fed observes three primary funding market indices: the Effective Federal Funds Rate (EFFR), Tri-Party General Collateral Rate (TGCR), and Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR). While the EFFR has remained relatively stable around 4.83% following a reduction, both the TGCR and SOFR have experienced yield spikes in recent months. Such movements suggest a growing divergence in market rates and emphasize that the funding market experiences periodic strain, particularly when excess liquidity begins to wane.
In conclusion, the drastic decline in ON RRP balances, accompanied by the stability of reserve balances, suggests a gradual normalization within the Fed’s financial framework. High focus on the temporary rate pressures elucidates a shift towards better resource allocation within the markets. The proactive measures taken by the Fed in both QE and QT cycles reveal an ongoing effort to manage liquidity effectively and maintain a balanced economic environment. The commentary from Fed officials, particularly Lorie Logan, underscores the importance of monitoring these transient pressures as they contribute to the overarching health of financial markets, creating a dynamic landscape where liquidity can be effectively redistributed to align with market demands.